基于OpenVINO与PaddleOCR的输出抄表器
 openlab_4276841a
更新于 2年前
openlab_4276841a
更新于 2年前
项目视频介绍回放
尽情期待活动回放视频
背景介绍
“表”是生活中的随处可见的一种设备。常见的“表”包括了家用电表,水表等设备;除此之外,还有工频场强计等“表”。受制于由于受到区域因素以及技术因素的制约,并非每种“表”都能够进行数据的自动采集,从而只能通过人工手动抄表。这种数据采集工作一方面较为费事和枯燥,另一方面,长时间工作带来的会导致工作人员疲劳,从而产生抄录错误。通过人工智能技术构造自动化的抄表流程能够极大的克服上述问题,提高工作效率。相关工作
迄今为止,已经有许多关于电表读数的优秀项目出现,这些项目大都依赖于对特定场景的模型训练(包括微调)。例如:
·【PaddlePaddle+OpenVINO】电表检测识别模型的部署
· OpenVINO meter reader
但对于抄表工作的业务场景而言,具有以下特点:
无法准备大量的彻底贴合业务场景的数据集。
待抄录的“表”中的内容是文字,而非进度条或仪表盘
基于开放数据训练得到的OCR模型能够识别到“表”中的内容
因而,对于一些较为规整的“表”,我们完全可以基于开源OCR模型进行零微调的抄表工作。
技术方案
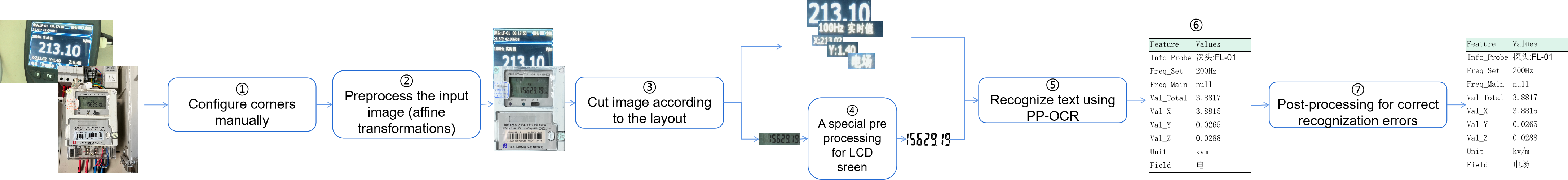
本项目提供了有一种无需额外训练的抄表器,只需要人为指定一些和布局有关的配置信息,即可实现表中数据的记录。总体流程如下:1、配置图片中屏幕区域的坐标值。(这些坐标值也可以通过cv2的拐点检测或深度学习进行获取)
2、对图片进行预处理(仿射变换)
3、配置待识别的元素对应的坐标,并裁剪对应的区域。
4、如有需要,可以对裁剪下来的区域进行预处理。
5、基于OpenVINO进行文字识别。
6、结构化输出信息
7、如有需要,对输出结果进行进一步精炼。
目录
1、背景介绍2、图片预处理
3、基于OpenVINO加载PaddleOCR识别模型进行预测
4、结构化输出与后处理
图片预处理
由于本项目是一个零微调的项目,因此,为了保证识别模型的有效性,需要人工对齐输入信息。· 修正倾斜的图片,将图片中的屏幕区域修正到指定的大小
· 根据从说明书等地方获取到的设备信息,设定待识别的区域在屏幕上的布局。
修正图片
以下列图片为例,本节展示如何将图片从倾斜的状态,修正为正面观众的状态。
In [3]
# 配置坐标信息
# The coordinates of the corners of the screen in case 1
POINTS = [[1121, 56], # Left top
[3242, 183], # right top
[3040, 1841], # right bottom
[1000, 1543]] # left bottom
# The size of the screen in case 1
DESIGN_SHAPE = (1300, 1000) In [5]
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 定义仿射变换函数
def pre_processing(img, point_list, target_shape):
"""
Preprocessing function for normalizing skewed images.
Parameters:
img (np.ndarray): Input image.
point_list (List[List[int, int], List[int, int], List[int, int]]): Coordinates of the corners of the screen.
target_shape (Tuple(int, int)): The design shape.
"""
# affine transformations
# point list is the coordinates of the corners of the screen
# target shape is the design shape
target_w, target_h = target_shape
pts1 = np.float32(point_list)
pts2 = np.float32([[0, 0],[target_w,0],[target_w, target_h],[0,target_h]])
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1, pts2)
img2 = cv2.warpPerspective(img, M, (target_w,target_h))
return img2 In [6]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 执行预处理
img = cv2.imread('example1.jpg')
# affine transformations to normalize skewed images
img = pre_processing(img, POINTS, DESIGN_SHAPE)
# The screen part is cropped and corrected
plt.imshow(img)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7fa87a3e9510>
<Figure size 640x480 with 1 Axes>
基于OpenVINO加载PaddleOCR识别模型进行预测
文字识别模型(PaddleOCR)
PaddleOCR 是PaddlePaddle的文字识别套件。迄今为止,PaddleOCR已经提供了许多复用性强的预训练模型。在本项目中使用的预训练模型是Chinese and English ultra-lightweight PP-OCR model (9.4M)。更多的信息请参考PaddleOCR Github或PaddleOCR Gitee。一个标准的OCR流程包括了文字检测和文字识别,对于本项目来说,文字检测工作已经通过人工配置的方式解决了,因此,只需要进行文字识别即可。
OpenVINO简介
OpenVINO作为Intel原生的深度学习推理框架,可以最大化的提升人工智能神经网络在Intel平台上的执行性能,实现一次编写,任意部署的开发体验。OpenVINO在2022.1版本后,就可以直接支持飞桨模型,大大提升了模型在Intel异构硬件上的推理性能与部署便捷性,带来更高的生产效率,更广阔的兼容性以及推理性能的优化。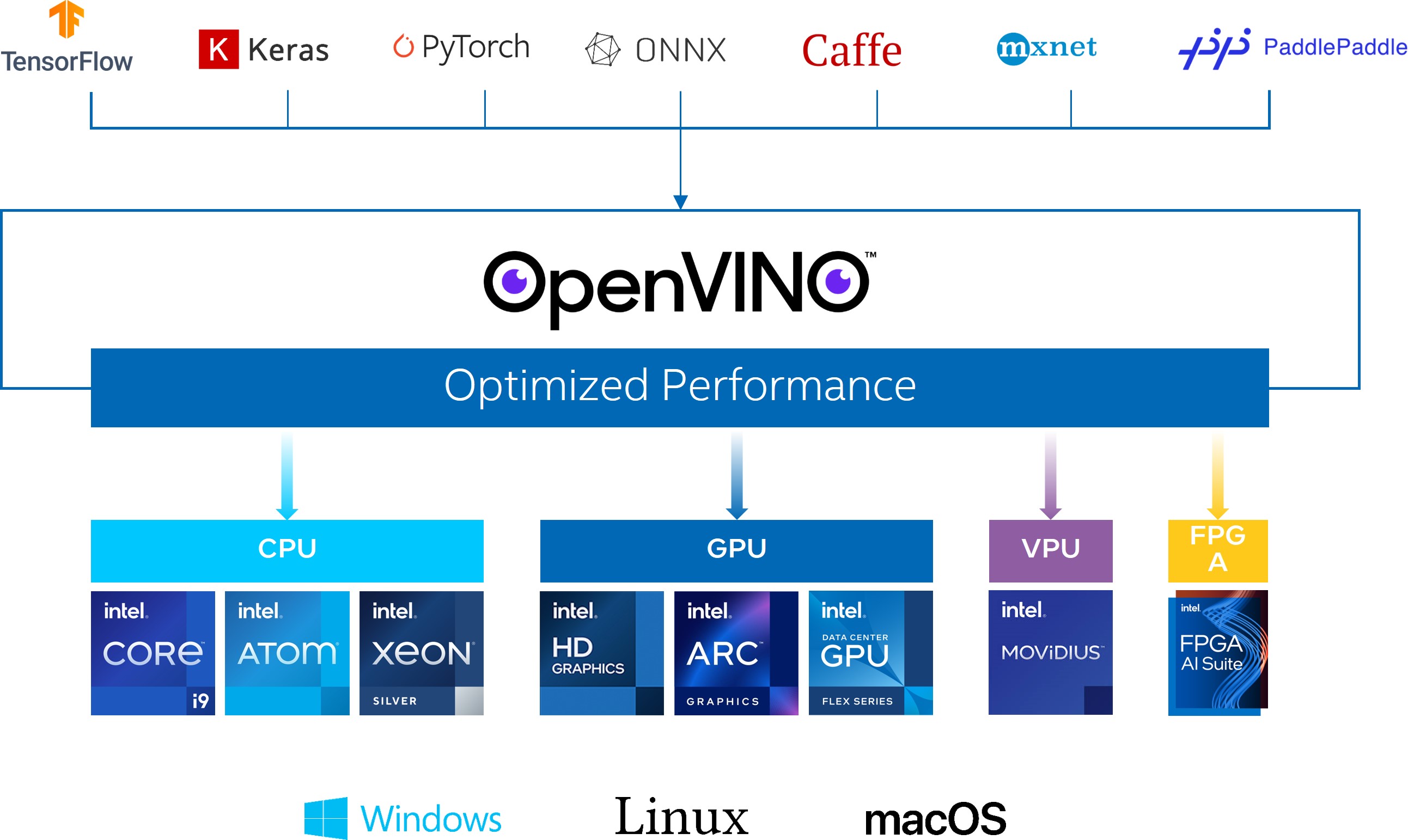
获取模型
In [ ]! wget "https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar"
! tar -xvf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar 基于OpenVINO加载PaddleOCR
使用OpenVINO加载Paddle模型无需经过任何转换,只需要1、创建环境
2、读取模型
3、生成推理接口
In [ ]
! pip install openvinoIn [11]
from openvino.runtime import Core
# Initialize OpenVINO Runtime for text recognition.
core = Core()
# Read the model and corresponding weights from a file.
rec_model_file_path = "ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer/inference.pdmodel"
rec_model = core.read_model(model=rec_model_file_path)
# Assign dynamic shapes to every input layer on the last dimension.
for input_layer in rec_model.inputs:
input_shape = input_layer.partial_shape
input_shape[3] = -1
rec_model.reshape({input_layer: input_shape})
rec_compiled_model = core.compile_model(model=rec_model, device_name="CPU")
# Get input and output nodes.
rec_input_layer = rec_compiled_model.input(0)
rec_output_layer = rec_compiled_model.output(0) 文字识别
依旧对于上述示例图片,希望结构化输出以下内容:[{"Info_Probe":""}, {"Freq_Set":""}, {"Freq_Main":""}, {"Val_Total":""},{"Val_X":""}, {"Val_Y":""}, {"Val_Z":""}, {"Unit":""}, {"Field":""}]。输出示例如下图所示:
配置布局
首先,需要基于仿射变换的结果,配置各个元素在图片上的布局。这个配置对于同一批表来说是固定的。
In [13]
# features and layout information
DESIGN_LAYOUT = {'Info_Probe':[14, 36, 410, 135], # feature_name, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax
'Freq_Set':[5, 290, 544, 406],
'Val_Total':[52, 419, 1256, 741],
'Val_X':[19, 774, 433, 882],
'Val_Y':[433, 773, 874, 884],
'Val_Z':[873, 773, 1276, 883],
'Unit':[1064, 291, 1295, 403],
'Field':[5, 913, 243, 998]} In [18]
import copy
import math
# Preprocess for text recognition.
def resize_norm_img(img, max_wh_ratio):
"""
Resize input image for text recognition
Parameters:
img: image with bounding box from text detection
max_wh_ratio: ratio of image scaling
"""
rec_image_shape = [3, 48, 320]
imgC, imgH, imgW = rec_image_shape
assert imgC == img.shape[2]
character_type = "ch"
if character_type == "ch":
imgW = int((32 * max_wh_ratio))
h, w = img.shape[:2]
ratio = w / float(h)
if math.ceil(imgH * ratio) > imgW:
resized_w = imgW
else:
resized_w = int(math.ceil(imgH * ratio))
resized_image = cv2.resize(img, (resized_w, imgH))
resized_image = resized_image.astype('float32')
resized_image = resized_image.transpose((2, 0, 1)) / 255
resized_image -= 0.5
resized_image /= 0.5
padding_im = np.zeros((imgC, imgH, imgW), dtype=np.float32)
padding_im[:, :, 0:resized_w] = resized_image
return padding_im
def get_rotate_crop_image(img, points):
'''
img_height, img_width = img.shape[0:2]
left = int(np.min(points[:, 0]))
right = int(np.max(points[:, 0]))
top = int(np.min(points[:, 1]))
bottom = int(np.max(points[:, 1]))
img_crop = img[top:bottom, left:right, :].copy()
points[:, 0] = points[:, 0] - left
points[:, 1] = points[:, 1] - top
'''
assert len(points) == 4, "shape of point***ust be 4*2"
img_crop_width = int(
max(
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[1]),
np.linalg.norm(points[2] - points[3])))
img_crop_height = int(
max(
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[3]),
np.linalg.norm(points[1] - points[2])))
pts_std = np.float32([[0, 0], [img_crop_width, 0],
[img_crop_width, img_crop_height],
[0, img_crop_height]])
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(points, pts_std)
dst_img = cv2.warpPerspective(
img,
M, (img_crop_width, img_crop_height),
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE,
flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
dst_img_height, dst_img_width = dst_img.shape[0:2]
if dst_img_height * 1.0 / dst_img_width >= 1.5:
dst_img = np.rot90(dst_img)
return dst_img
def prep_for_rec(dt_boxes, frame):
"""
Preprocessing of the detected bounding boxes for text recognition
Parameters:
dt_boxes: detected bounding boxes from text detection
frame: original input frame
"""
ori_im = frame.copy()
img_crop_list = []
for bno in range(len(dt_boxes)):
tmp_box = copy.deepcopy(dt_boxe***no])
img_crop = get_rotate_crop_image(ori_im, tmp_box)
img_crop_list.append(img_crop)
img_num = len(img_crop_list)
# Calculate the aspect ratio of all text bars.
width_list = []
for img in img_crop_list:
width_list.append(img.shape[1] / float(img.shape[0]))
# Sorting can speed up the recognition process.
indices = np.argsort(np.array(width_list))
return img_crop_list, img_num, indices
def batch_text_box(img_crop_list, img_num, indice****eg_img_no, batch_num):
"""
Batch for text recognition
Parameters:
img_crop_list: processed bounding box images with detected bounding box
img_num: number of bounding boxes from text detection
indices: sorting for bounding boxes to speed up text recognition
beg_img_no: the beginning number of bounding boxes for each batch of text recognition inference
batch_num: number of images in each batch
"""
norm_img_batch = []
max_wh_ratio = 0
end_img_no = min(img_num, beg_img_no + batch_num)
for ino in range(beg_img_no, end_img_no):
h, w = img_crop_list[indices[ino]].shape[0:2]
wh_ratio = w * 1.0 / h
max_wh_ratio = max(max_wh_ratio, wh_ratio)
for ino in range(beg_img_no, end_img_no):
norm_img = resize_norm_img(img_crop_list[indices[ino]], max_wh_ratio)
norm_img = norm_img[np.newaxis, :]
norm_img_batch.append(norm_img)
norm_img_batch = np.concatenate(norm_img_batch)
norm_img_batch = norm_img_batch.copy()
return norm_img_batch 用于将文字识别的结果进行解码,转化为汉字
In [21]
class RecLabelDecode(object):
""" Convert between text-label and text-index """
def __init__(self,
character_dict_path=None,
character_type='ch',
use_space_char=False):
support_character_type = [
'ch', 'en', 'EN_symbol', 'french', 'german', 'japan', 'korean',
'it', 'xi', 'pu', 'ru', 'ar', 'ta', 'ug', 'fa', 'ur', 'rs', 'oc',
'rsc', 'bg', 'uk', 'be', 'te', 'ka', 'chinese_cht', 'hi', 'mr',
'ne', 'EN', 'latin', 'arabic', 'cyrillic', 'devanagari'
]
assert character_type in support_character_type, "Only {} are supported now but get {}".format(
support_character_type, character_type)
self.beg_str = "sos"
self.end_str = "eos"
if character_type == "en":
self.character_str = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
dict_character = list(self.character_str)
elif character_type == "EN_symbol":
# same with ASTER setting (use 94 char).
self.character_str = string.printable[:-6]
dict_character = list(self.character_str)
elif character_type in support_character_type:
self.character_str = []
assert character_dict_path is not None, "character_dict_path should not be None when character_type is {}".format(
character_type)
with open(character_dict_path, "rb") as fin:
lines = fin.readlines()
for line in lines:
line = line.decode('utf-8').strip("\n").strip("\r\n")
self.character_str.append(line)
if use_space_char:
self.character_str.append(" ")
dict_character = list(self.character_str)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
self.character_type = character_type
dict_character = self.add_special_char(dict_character)
self.dict = {}
for i, char in enumerate(dict_character):
self.dict[char] = i
self.character = dict_character
def __call__(self, preds, label=None, *args, **kwargs):
preds_idx = preds.argmax(axis=2)
preds_prob = pred***ax(axis=2)
text = self.decode(preds_idx, preds_prob, is_remove_duplicate=True)
if label is None:
return text
label = self.decode(label)
return text, label
def add_special_char(self, dict_character):
dict_character = ['blank'] + dict_character
return dict_character
def decode(self, text_index, text_prob=None, is_remove_duplicate=False):
""" convert text-index into text-label. """
result_list = []
ignored_tokens = self.get_ignored_tokens()
batch_size = len(text_index)
for batch_idx in range(batch_size):
char_list = []
conf_list = []
for idx in range(len(text_index[batch_idx])):
if text_index[batch_idx][idx] in ignored_tokens:
continue
if is_remove_duplicate:
# only for predict
if idx > 0 and text_index[batch_idx][idx - 1] == text_index[
batch_idx][idx]:
continue
char_list.append(self.character[int(text_index[batch_idx][
idx])])
if text_prob is not None:
conf_list.append(text_prob[batch_idx][idx])
else:
conf_list.append(1)
text = ''.join(char_list)
result_list.append((text, np.mean(conf_list)))
return result_list
def get_ignored_tokens(self):
return [0] # for ctc blank
# Since the recognition results contain chinese words, we should use 'ch' as character_type
text_decoder = RecLabelDecode(character_dict_path="ppocr_keys_v1.txt",
character_type='ch',
use_space_char=True) 下面以Freq_Set为例,进行文字识别
In [25]
# 输出结构体
struct_result = {}
# Crop imgs according the layout information
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = DESIGN_LAYOUT['Freq_Set']
crop_img = img[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
h = ymax - ymin # height of crop_img
w = xmax - xmin # width of crop_img
dt_boxes = [np.array([[0,0],[w,0],[w,h],[0,h]],dtype='float32')]
batch_num = 1
# since the input img is cropped, we do not need a detection model to find the position of texts
# Preprocess detection results for recognition.
img_crop_list, img_num, indices = prep_for_rec(dt_boxes, crop_img)
# txts are the recognized text results
rec_res = [['', 0.0]] * img_num
txts = []
for beg_img_no in range(0, img_num):
# Recognition starts from here.
norm_img_batch = batch_text_box(
img_crop_list, img_num, indice****eg_img_no, batch_num)
# Run inference for text recognition.
rec_results = rec_compiled_model([norm_img_batch])[rec_output_layer]
# Postprocessing recognition results.
rec_result = text_decoder(rec_results)
for rno in range(len(rec_result)):
rec_res[indice***eg_img_no + rno]] = rec_result[rno]
if rec_res:
txts = [rec_res[i][0] for i in range(len(rec_res))]
# record the recognition result
struct_result['Freq_Set'] = txts[0]
print(txts[0]) 上面的逻辑已经完成了使用OpenVINO加载PaddleOCR并进行预测,但实际上由于整个模型没有进行微调,所以对于当前的业务场景来说可能不够完美,这个时候可以通过一些简单的逻辑进行处理,比如,对于示例图片中,H2必然是不存在的,这个地方可以直接通过replace替换为HZ。
简单来说,对于示例图片的这种表,可以定义如下后处理函数:
In [28]
# Post-processing, fix some error made in recognition
def post_processing(results, post_configration):
"""
Postprocessing function for correcting the recognition errors.
Parameters:
results (Dict): The result directory.
post_configration (Dict): The configuration directory.
"""
for key in results.keys():
if len(post_configration[key]) == 0:
continue # nothing to do
for post_item in post_configration[key]:
key_word = post_item[0]
if key_word == 'MP': # mapping
source_word = post_item[1]
target_word = post_item[2]
if source_word in results[key]:
results[key] = target_word
elif key_word == 'RP': # removing
source_word = post_item[1]
target_word = post_item[2]
results[key] = results[key].replace(source_word, target_word)
elif key_word == 'AD': # add point
add_position = post_item[1]
results[key] = results[key][:add_position] + '.' + results[key][add_position:]
return results
# 通过配置决定如何进行后处理
# Congiguration for postprocessing of the results
RESULT_POST = {"Info_Probe":[['MP', 'LF', '探头:LF-01']], # words need to be mapped
"Freq_Set":[['RP', '实时值', ''], ['RP', ' ', ''], ['RP', 'H2', 'HZ']], # words need to be replace
"Val_Total":[['RP', 'H2', 'Hz']],
"Val_X":[['RP', 'X', ''], ['RP', ':', '']],
"Val_Y":[['RP', 'Y', ''], ['RP', ':', '']],
"Val_Z":[['RP', 'Z', ''], ['RP', ':', '']],
"Unit":[['MP', 'T', 'μT'],['MP', 'kV', 'kV/m'],['MP', 'kv', 'kV/m'],['MP', 'vm', 'V/m'],['MP', 'Vm', 'V/m'],['MP', 'A', 'A/m']],
"Field":[]} # nothing need to do
# Postprocessing, to fix some error made in recognition
struct_result = post_processing(struct_result, RESULT_POST)
# Print result
print(struct_result)
{'Freq_Set': '100HZ'} 为了方便运行,这里也提供了一个封装好的函数
In [32]
# 为了避免因为图片模糊导致的漏检,配置一个输出模板,从而让每个图片输出格式都一致
# Output template in case 1
RESULT_TEMP = {"Info_Probe":"探头:---",
"Freq_Set":"",
"Val_Total":"无探头",
"Val_X":"",
"Val_Y":"",
"Val_Z":"",
"Unit":"A/m",
"Field":"常规"} # the input of recognition should be image, DESIGN information, compiled_model
def main_function(img, DESIGN_LAYOUT, RESULT_TEMP, preprocess_function=None):
"""
Main program of processing the meter.
Parameters:
img (np.ndarray): Input image.
DESIGN_LAYOUT (Dict): The coordinates of elements in the screen.
RESULT_TEMP (Dict): The template for structure output.
preprocess_function: The preprocess function for cropped images, `None` means no preprocessing to do.
"""
# copy the structure output template
struct_result = copy.deepcopy(RESULT_TEMP)
# structure recognition begins here
for key in DESIGN_LAYOUT.keys():
# Crop imgs according the layout information
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = DESIGN_LAYOUT[key]
crop_img = img[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
# preprocessing for cropped images
if preprocess_function is not None:
crop_img = preprocess_function(crop_img)
h = ymax - ymin # height of crop_img
w = xmax - xmin # width of crop_img
dt_boxes = [np.array([[0,0],[w,0],[w,h],[0,h]],dtype='float32')]
batch_num = 1
# since the input img is cropped, we do not need a detection model to find the position of texts
# Preprocess detection results for recognition.
img_crop_list, img_num, indices = prep_for_rec(dt_boxes, crop_img)
# txts are the recognized text results
rec_res = [['', 0.0]] * img_num
txts = []
for beg_img_no in range(0, img_num):
# Recognition starts from here.
norm_img_batch = batch_text_box(
img_crop_list, img_num, indice****eg_img_no, batch_num)
# Run inference for text recognition.
rec_results = rec_compiled_model([norm_img_batch])[rec_output_layer]
# Postprocessing recognition results.
rec_result = text_decoder(rec_results)
for rno in range(len(rec_result)):
rec_res[indice***eg_img_no + rno]] = rec_result[rno]
if rec_res:
txts = [rec_res[i][0] for i in range(len(rec_res))]
# record the recognition result
struct_result[key] = txts[0]
return struct_result img = cv2.imread('example1.jpg')
# affine transformations to normalize skewed images
img = pre_processing(img, POINTS, DESIGN_SHAPE)
struct_result = main_function(img, DESIGN_LAYOUT, RESULT_TEMP)
# Postprocessing, to fix some error made in recognition
struct_result = post_processing(struct_result, RESULT_POST)
# Print result
print(struct_result)
{'Info_Probe': '探头:LF-01', 'Freq_Set': '100HZ', 'Val_Total': '734.57', 'Val_X': '734.53', 'V
0个评论

